- 29th Feb 2024
- 06:03 am
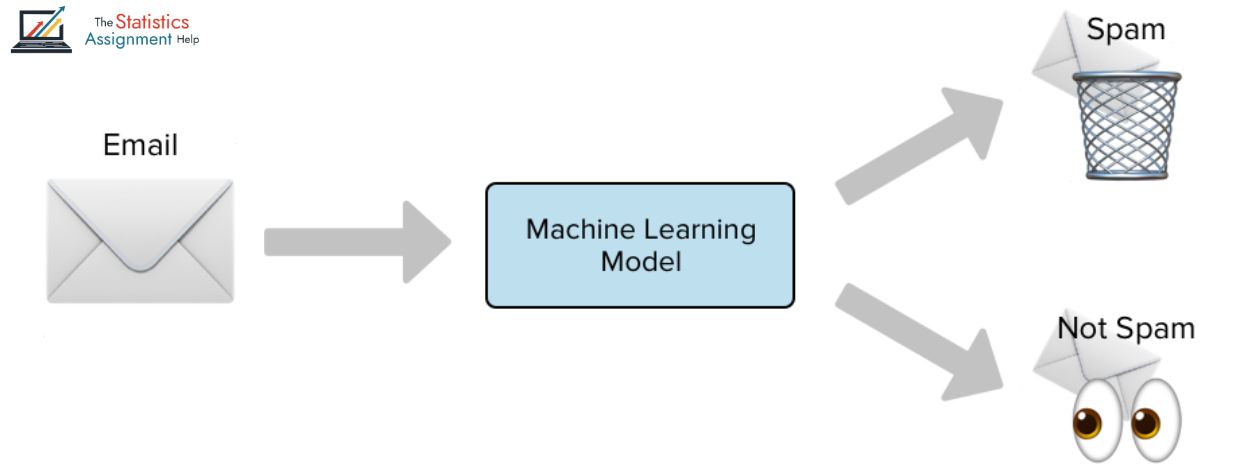
Emails play a vital role in everyday experience, yet with the exchange of valuable correspondences come the clutters of spam emails with inherent security threats. In order to check such, spam filters apply machine learning techniques, particularly text classification, to automatically identify and block spam.
In this blog, we’ll explain how text classification works in email filtering and the key steps involved in building an effective spam detection system.
What Is Text Classification?
Text classification is a machine learning technique of labeling text with pre-conceived categories. In the case of email filtering, one is to ensure that the email is labeled either as spam or not spam. This is usually accomplished through supervised learning where models are trained on a set of data that already have labeled exemplars of spam, and non-spam email.
Text classification does not only refer to spam detection and its applications are popular in sentiment analysis, topic detection and customer feedback analysis. However, email classification is one of its most practical and widely adopted applications.
Steps in Email Spam Classification
1. Preprocessing the Text
Before training a model, emails must be cleaned and prepared for analysis. This includes:
- Removing noise like punctuation, symbols, and HTML tags.
- Tokenization: Splitting text into words or phrases.
- Lowercasing all words to ensure consistency.
- Removing stopwords (e.g., “and,” “is”) that don’t add value to classification.
- Stemming or lemmatization to reduce words to their root form, such as converting “running” and “runs” to “run.”
These steps make the data more manageable and meaningful for the model.
2. Feature Extraction
The text is translated into numerical form which is comprehended by the model after being preprocessed. A popular approach is the bag-of-words model where each email can be modeled as a vector whose terms depend on the frequencies of words.
Other methods such as TF-IDF would place greater importance on those words of special significance to a set of email messages that turn out to be infrequent in absolute terms. These representations of the feature enable the model to identify patterns that show that the message is spam.
3. Choosing a Classification Model
There are a number of models of machine learning that are usually applied in spam detection:
- Naive Bayes: Very fast and powerful should be fast at least on text data.
- Support Vector Machines (SVMs): They excel at creating a boundary between the spam and non-spam in high dimensional datasets.
- Decision Trees / Random Forests: You could employ this in case you wish to enhance accuracy with the help of several decision paths.
Depending on complexity (size or difficulty) and performance requirements, the dataset will depend on which model to use.
4. Evaluating and Tuning the Model
After training, the model’s performance is evaluated using metrics like:
- Accuracy – overall correctness
- Precision and Recall – how well it avoids false positives and false negatives
- F1-score – the balance between precision and recall
Given the results, hyperparameters can be modified in the interest of performance. Cross-validation also assists in ensuring good performance of the model on unseen data.
5. Deployment and Integration
Once ready, the model is deployed into email systems where it checks incoming messages in real time. It must be integrated smoothly to classify emails quickly and accurately.
User feedback is also important. If users mark emails as spam or not spam, this information can be used to improve future predictions by retraining the model with updated data.
Keeping the Model Updated
Spam strategies are always changing. New types of messages appear regularly, so the spam detection model needs frequent updates.
This means retraining with new examples and monitoring the model’s performance over time. Regular updates ensure it keeps detecting spam accurately and adjusting to new trends.
Conclusion
Text classification has become an efficient method in filtering of spam and coming up with safe and efficient communication. Machine learning models are able to detect a pattern, and respond to emerging threats, learning. Whether it is preprocessing and feature extraction or choosing the appropriate model, each step is significant in spam detection.
To a student and a researcher, spam filtering provides a demonstration of the actual use of text classification. In case you work with data or require assistance in similar tasks, services such as STATA Assignment Help can help you understand how to build a model, analyze it, and apply to the project, simplifying the learning process and making it more effective.








