- 29th Feb 2024
- 06:03 am
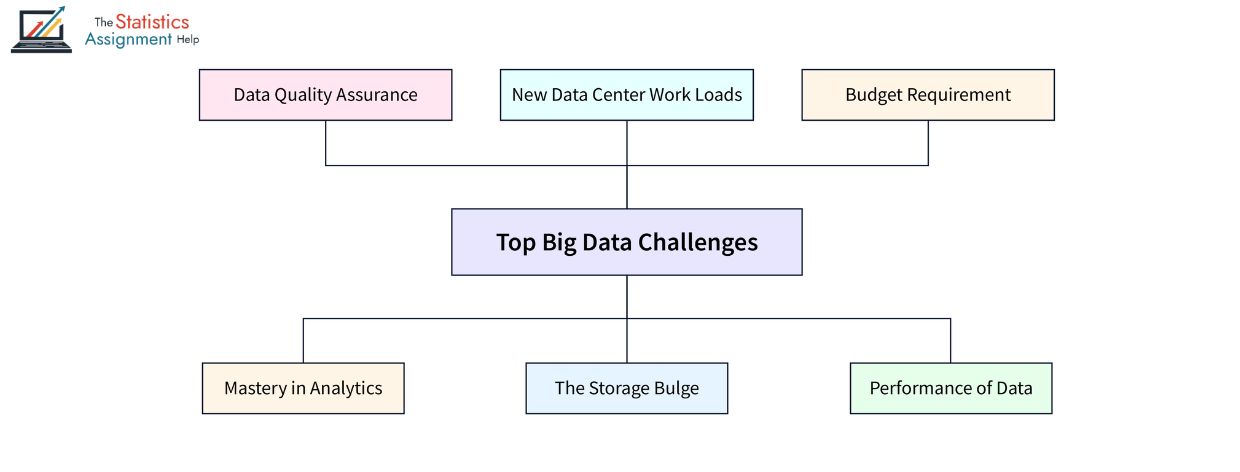
As of today, in the digital era, organizations are gathering data more intensively than ever. Although this presents new opportunities to extract new knowledge and make wiser business moves, it comes with its fair share of challenges particularly with regards to data storage and handling such large volumes of information. The big data analytics is an essential process in transforming this information into understanding, unlike the fact that without appropriate storage and management schemes, the real worth of it is seemingly impossible. This is why people are resorting to big data analytics assignment help, data analytics homework help, or contacting online data analytics specialists who will do a better job of managing these burgeoning needs.
Understanding Big Data
To put it simply, big data refers to extremely large and complex datasets that can’t be managed using traditional methods. It is usually defined by three key traits:
- Volume: The huge amount of data created within sources such as social media, sensors, websites and transactions.
- Velocity: The rate of data generation and its demand to be processed, which is often on real-time.
- Variety: The various formats data may be produced in, such as structured (such as spreadsheets), semi-structured (such as XML files), and unstructured (such as videos or even social media posts).
These features render big data powerful and challenging to manage.
Key Challenges in Data Storage
Managing the storage of big data is not a simple task. Organizations face multiple storage-related issues, including:
- Scalability: Traditional storage systems may struggle to grow alongside data volumes. Cloud storage and distributed systems like HDFS are now widely used for their ability to scale easily.
- Cost Management: Setting up and operating huge storage data systems may be costly. Cloud computing solutions are much cheaper and flexible with pay-as-you-go options available.
- Security Risks: The greater the data, the greater the danger of cyber-attacks and information breaches. To secure sensitive information, it is important to have access control and stringent guidelines through the use of encryption.
- Data Overflow: The analysis may become more challenging due to the continuous incoming data which may overwhelm the systems.
- Fragmented Storage: Information is frequently dispersed and locked within various systems and fronts thereby posing challenges on efficient access as well as management.
- Compliance Issues: Companies must follow strict industry rules on how and where data is stored, which provides complexity.
- Performance Demands: Users expect quick access and treatment, which can be difficult with large and growing datasets.
- Outdated Infrastructure: Many companies still depend on older systems that cannot follow modern data storage needs.
Major Challenges in Data Management
In addition to storage, managing big data brings its own set of challenges:
- Too Much Data: It is difficult to handle, filter, and use due to the sheer amount of data involved.
- Security Concerns: The most important concern is to keep the data safe by defending it against illegal access and keep it confidential.
- Poor Data Quality: Either misleading or incomplete figures result to poor decisions. It is important to make it consistent and accurate.
- Lack of Governance: There should be clear policies and controls to be followed regarding the use and sharing of data.
- Difficult Integration: Integration of different sources of data into a single system is a technically difficult yet mandatory process.
- Storage Issues: Effective storage solutions are needed with a low cost and ability to scale up with data volumes.
- Privacy Regulations: It is more important than ever to take care of personal data and act in accordance with such legislation as GDPR.
- Advanced Analytics: To acquire the information, AI or machine learning needs clean and well-organized information, and this is challenging to achieve without control.
Conclusion
An important element to developing the value of big data analytics is being able to manage and store data effectively. With organizations creating increasingly large quantities of information, issues of scalability, security, compliance and performance become even more urgent. In order to overcome these difficulties it is necessary not only to match technology but also have a solid grasp of principles of data management.
It is a complex area, and the need to find the right guidance in this direction can be hugely helpful to students and even professionals who need guidance in this area by seeking the assistance of SPSS Assignment Help, STATA Assignment Help, Data Analytics Assignment Help, Machine Learning Assignment Help, and Econometrics Assignment Help. These professional services take great assistance in learning the provision of analytical tools, the application of data-driven solutions, and the ability to keep abreast with the changing industry processes.
About The Author:
- Name: Dr. Lisa K.
- Qualification: Ph.D. in Big Data Analytics
- Expertise: Achieved success at solving the problems of data storage and management within the field of Big Data Analytics.
- Research Focus: Dr. Lisa K. has been one of the finest sources that a professional and researcher can offer answers to the questions confronting the Big Data Analytics in the reference to the issues of the data storage and manageability.
- Practical Experience: Translates practical wisdom gained via team-ups with talents of the industry, to make them applicable in the real world. Dr. Lisa K will be the go-to guide to use in navigating in any given field that involves big data analytics especially the field of data storage and management issue.








